GATE Study Planner Electrical Engineering(EE)
Introduction
Hi Warriors,
Please find a comprehensive GATE Study Plan for your GATE exam 2022 preparation. The number of hours considered in this planner is 3 hours per day (on an average). You can adjust number of hours as per your convenience. For instance, if you see the Master planner below, you will find we need approx. 220-250 hours for completing Stage-I. So if we study 3 hours, on an average, for 90 days = 270 hours, we can easily cover what’s given in the document.
Note: This plan is designed in consideration with students who have got top 100 ranks in GATE or any national level exam in the past few years
A similar plan is followed by many exam toppers and is highly recommended by most of The top faculties of the country. You will realize while going through it that a lot of research is gone In to make it helpful to you.
The following document contains:
- Master plan
- Flow of a subject which should be followed
- How to make notes
- How to do Test Analysis
- How to do revision
- Subject wise( topic wise) time devotion plan
1.Master Plan
| Stage – I | Stage – II | Stage – III | Stage – IV | Stage – V | |
| Notes + Gate Ques + Topic Test + Subject Test | GA = 27 hrs
Maths = 44 hrs EM = 46 hrs FM = 69 hrs SOM = 68 hrs
|
Thermo = 79 hrs
Manufacturing = 77 hrs TOM = 64 hrs |
MD = 40 hrs
HT = 52 hrs IE = 59 hrs |
3 FLT | 3 FLT |
| Extra Workout | One Mock with Analysis = 7 hrs | 2 Mocks with Analysis = 15 hrs | 3 Mocks | 3 Mocks | |
| Revise all 8 Subjects = 130 hrs | Revise all Subjects = 120 hrs | Revision 2 | Revision 3 | ||
| Total Hours | 254 | 357 | 286 | 125 | 140 |
2. Flow of Studies for Any subject:
- Notes
- GATE que for past 10 years topic wise
- Topic wise test on aspiration.ai
- Subject tests on aspiration.ai
- Extra practice que + revision of subject
3.How to Make Notes:
- If you attend lectures of any faculty through GATEFLIX then you can easily make notes. If you haven’t done so, go to online videos to do so. You may also go to Youtube:- Khan academy, Nptel or the latest and most popular are Gateflix videos.
- Make notes neatly as they will be very very useful while revision in the last 30 days. Use 3 colour pen to indicate important, very important and very very important concepts.
- Make a separate handbook for formulas. In exams 40% questions are direct formula based or implied formula based. Problem with students is that they tend to mix up formula. If you have this handbook of formula ready and have revised the things at least 2 times , I can guarantee you the 40 % marks.
- Don’t Xerox someone’s notes because the moment you write yourself then you can memorize the concept for a longer duration.
- Leave one page Space after 2/3 pages or after every major chapter. This is to ensure that if you come across any vital formula or Information or short trick while referring tests or reference book later then you may place That information in these spaces.
4.How to do a Test Analysis:
- Any test( Online or offline) need to taken in time frame.There is No point in taking the test without a time Limit.
- Don’t take any test without revision of Notes of the syllabus covered in the test. It will be a wastage if You just randomly take a test.
- Once the test time is over, don’t jump to answer Solution . Check the answer key and get To Know your score.
- Now follow a 3 stage process .
Stage 1: Go to the right ones and check whether you were confident of answering that question . If the answer is “yes” check the solution given in order to see which method was better( yours or the given in Book or online portal ). Adopt the best you like.
Stage 2: Go to questions which you got wrong. Try to fight with the question that why you got it wrong without looking at the solution yet. Try 3 or 4 times by re reading the question or even refer notes. Maximum time it’s a silly mistake. These silly Mistakes can’t be zeroed but can be reduced by practicing more .Refer notes again if needed. In case you are still not able to click after a lot of Slumber, try to open the solution and check your mistake. If it was a new concept to you, add in the void space you have kept in your notes. This will help to solve similar question again.
Stage 3: Now the turn of questions which are unattempted.This could be due to
- Not knowing The concept or due to lack of time. If it was conceptual ignorance , go to your faculty ( many online live class teachers are available , In case you don’t have one)and learn the concept.
- It was a lack of time issue try now and solve it. If you are taking a lot of Time try to memorize few steps so that if it appears in exam you will be able to do it fast. Other students might leave such question in exam , But you will probably dare to attempt such and score more.
- The key to successs in any entrance exam is solve More , analyse more. In each subject you should Solve almost 1000+ questions including past year Actual Exam questions, topic wise test, subject test and mock tests.
5. How To do Revision:
- Well this is dependent on the way you have prepared notes and how effectively have you done the Test Analysis.
- Go through the whole cycle again in this revision phase like NOTES >- GATE QUESTIONS >- Topic test >- Subject Test >- Extra questions (if any ).
- While Revising, don’t solve Each and every question from notes or tests. Try To randomly pick 20 questions from different pages or test( purely random) . If you are able to recall the logic of 16+ then you are good to go ahead. If you are Not able to solve more than 10 questions then it’s a re revision time. Follow step 2.
- Try to have a bird eye view and See topics on which questions Are asked again and Again. Star mark them for making revision 2 and revision 3 effective.
6.SUBJECT WISE PLAN:
Below given is a detailed execution of the GATE study plan which carries subject wise in-depth action plan. In this artificial intelligence of GATE Study Planner, you will find:
- No of days and hours required to complete particular topics of particular subjects,
- No of times questions have been asked in GATE Exam for the last 10 years with the weightage of those questions.
a. General Aptitude
| Chapter 1 | Numerical Ability | Numerical computation, numerical estimation, numerical reasoning, data interpretation | 4 days |
| Chapter 2 | Verbal Ability | English grammar, sentence completion, verbal analogies, word groups, instructions, critical reasoning and verbal deductions | 2 days |
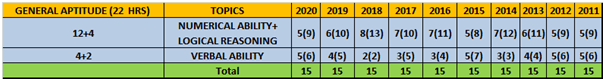
Note: For the years 2014 to 2017 there have been 2 and 3 sets so we have taken the average weightage of the topics for the same
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
GA Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 22 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 3 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 2 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 2 | ||
| Total | 29hrs |
b. Engineering Maths
| Chapter 1 | Linear Algebra | Matrix Algebra, Type of matrices, Determinant, Cramer’s rule, Systems of linear equations, Rank of the equation, consistency of the equation, Eigen values and Eigen vectors. |
2 day |
| Chapter 2 | Probability & distribution | Sampling theorems, Conditional probability, Baye’s theorem, Random variables, Expectation & Variance, Discrete and continuous distributions, uniform, normal, exponential, Poisson, Binomial. Correlation and regression analysis, covariance, correlation coefficient, Mean, median, mode and standard deviation |
1 day |
| Chapter 3 | Numerical methods | Solutions of non-linear algebraic equations, Newton Raphson method, Regulafalsi method or (method of false position), secant method, Gauss Elimination Method, Gauss Jordon method, Jacobi iteration method, Gauss Siedel iteration method, Numerical Integration: Trapezoidal rule, Simpson’s 1/3 & 3/8 rule, single and multi-step methods for differential equations, Euler’s method, RungeKutta Method |
1 day |
| Chapter 4 | Calculus | Limits & continuity, Basic differentiation & integration, Mean value theorems, Theorems of integral calculus, Evaluation of definite and improper integrals, Partial Derivatives, Maxima and minima, Multiple integrals, Vector identities, Directional derivatives, Line, Surface and Volume integrals, Stokes, Gauss and Green’s theorems. |
3 days |
| Chapter 5 | Differential Equations | First order equation (linear and nonlinear), Higher order linear differential equations with constant coefficients, Method of variation of parameters, Cauchy’s and Euler’s equations, Initial and boundary value problems, Partial Differential Equations and variable separable method. |
2 days |
| Chapter 6 | Complex Variables | Analytic functions, Cauchy’s integral theorem and integral formula, Taylor’s and Laurent series, Residue theorem |
1 day |
| Chapter 7 | Laplace Transforms
+ Fourier series |
Definition & property of Laplace transform + Fourier Series | 0.5 day |
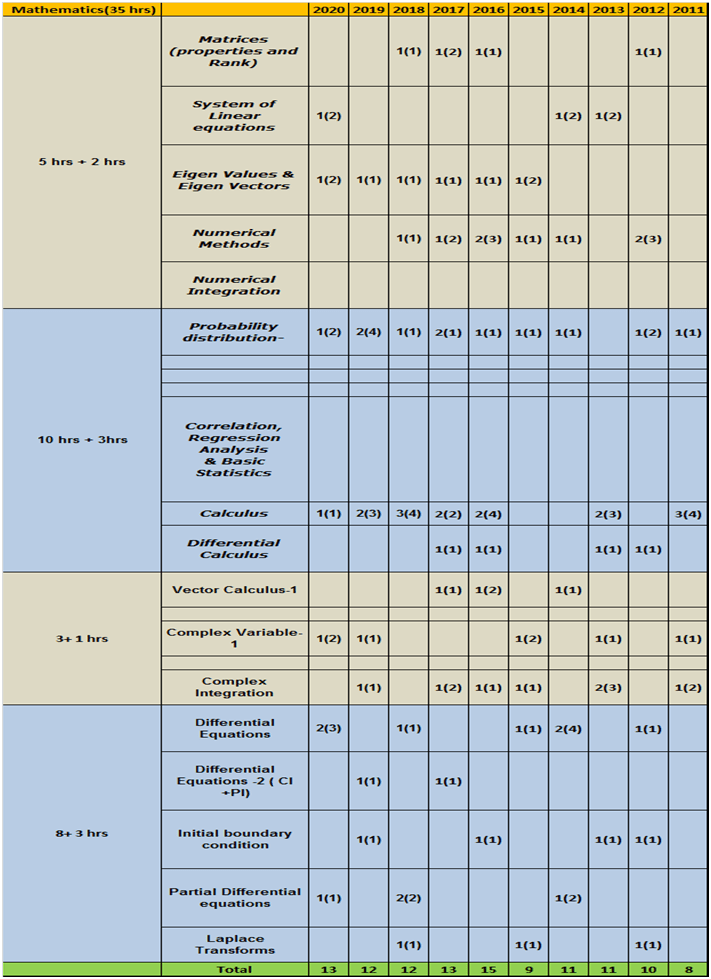
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Maths Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 35 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 5 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 6 | ||
| Total | 50 hrs |
c. Network Analysis/Circuit Theory
| Chapter 1 | Network Solution Methodology | Circuit elements, KCL, KVL, Nodal and mesh analysis, dependent & independent current & voltage sources, Network theorems: superposition, Thevenin and Norton’s, maximum power transfer, source conversion, Mcmillan theorem, Star-Delta transformation, reciprocity theorem |
4 days |
| Chapter 2 | Transient/Steady State Analysis of RLC Circuits to DC Input | Time domain analysis (steady state & Transient response) of RL, RC, RLC circuits, Time constant |
1 day |
| Chapter 3 | Sinusoidal Steady State Analysis | Sinusoidal excitation, phasor representation, RMS & average of periodic signal Steady state sinusoidal analysis using phasors, resonance, single phase/poly phase circuit analysis, Magnetically coupled circuits, |
1 day |
| Chapter 4 | Laplace Transform | Introduction to Laplace transform, TF of LTI system, Solution of network equations using Laplace transform: frequency domain analysis of RLC circuits. |
0.5 day |
| Chapter 5 | Two Port Networks | 2-port network parameters, Z/Y/H/ABCD/G parameter, reciprocity & Symmetry: driving point and transfer functions. State equations for networks., T & PI networks, interconnection of two port networks |
2 days |
| Chapter 6 | Network Topology | Matrices associated with graphs; nodal incidence, loop incidence, fundamental cut set and fundamental circuit matrices, applications in network |
1 day |
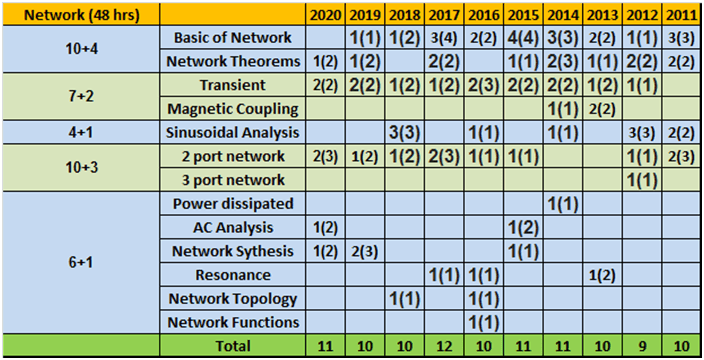
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Networks Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 48 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 5 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 8 | ||
| Total | 65 hrs |
d. Digital electronics
| Chapter 1 | Number systems and code conversions | Binary, octal, hex code, BCD code, Gray Code, Fixed – Point Representation and Floating Point Representation, 2’s complement |
2 days |
| Chapter 2 | Boolean algebra &Karnaugh maps | Boolean algebra, minimization of Boolean functions; Min term, SOP, POS |
|
| Chapter 3 | Logic Gates | Positive/ Negative level logic system, AND, OR, NOR, NAND, -OR, X-NOR, NOT gates, Realization of X – OR gate using NAND and NOR gates, bubbled AND/NOR gate, |
3 days |
| Chapter 4 | Logic Gates family | Digital IC families (DTL, TTL, ECL, MOS, CMOS). | |
| Chapter 5 | Combinational and Sequential digital Circuits | Combinatorial circuits: arithmetic circuits, code converters, multiplexers, decoders, PROMs and PLAs. Sequential circuits: latches and flip-flops, counters and shift-registers |
3 days |
| Chapter 6 | AD/DA Convertor | Sample and hold circuits, ADCs, DACs |
3 days |
| Chapter 7 | Semiconductor Memories
+ Microprocessor |
Volatile memory, Non Volatile memory, ROM, RAM, SRAM, DRAM, PROM, EEPROM, Memory device parameters or characteristics (Access time, random access, sequential access) Microprocessor (8085): architecture, programming, memory and I/O interfacing. |
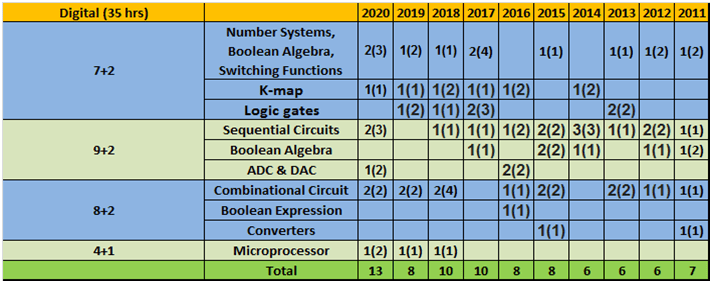
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Digital Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 35 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 3 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 3 | ||
| Total | 45 hrs |
e. Control System
| Chapter 1 | Basics of Control System | Basic control system components; block diagrammatic description, reduction of block diagrams. Open loop and closed loop (feedback) systems and stability analysis of these systems. Signal flow graphs and their use in determining transfer functions of systems; sensitivity; Modelling of control systems |
4 days |
| Chapter 2 | Time Domain Analysis | Type of standard Test signal, Transient and steady state analysis of LTI control systems and frequency response, over-damped, critically damped and under damped control systems, Type (0,1, 2, …) of the system & steady state error, peak time, Rise time, settling time and percentage overshoot; Characteristic equation |
|
| Chapter 3 | Stability &Routh Hurwitz Criterion | Concept of Stability, Tools and techniques for LTI control system analysis, Why Routh-Hurwitz criterion required? How to apply the RH criterion. |
|
| Chapter 4 | Root Locus Technique | Why Root locus Technique? Rules for Plotting the root loci, determining the stability condition by looking at the RL, Concept of complementary root locus(CRL) |
4 days |
| Chapter 5 | Frequency Response Analysis | Bode Plots, Polar plots and Nyquist plots. Gain Margin & Phase Margin, Relative stability; M and N circles; Nicholas chart |
|
| Chapter 6 | Compensators & Controllers | Control system compensators: elements of lead and lag compensation, elements of Proportional-Integral Derivative (PID) controller, PI, PD controller |
1 day |
| Chapter 7 | State Variable Analysis | State variable representation and solution of state equation of LTI control systems, state transition matrix, controllability & Observability |
2 days |
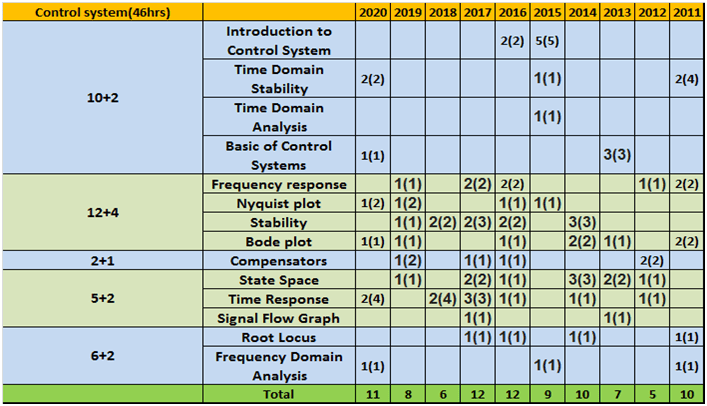
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Control Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 46 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 6 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 8 | ||
| Total | 64hrs |
f. Signal & System
| Chapter 1 | Basics Of Signal & Systems
|
Introduction to signals, classification of signals, important signals, classification of systems, different important types of systems. |
2 days |
| Chapter 2 | Lti System & Convolution
|
LTI system, frequency response of continuous LTI system filtering, convolution & its properties. |
3 days |
| Chapter 3 | Fourier Series & Fourier Transform
|
Trigonometric fourier series, complex form of fourier series, fourier transform, fourier transform of standard and continuous signal, properties of continuous time fourier transform, rayleigh’s energy and parseval’s power theorem |
3 days |
| Chapter 4 | Laplace Transform
|
Introduction, ROC & its properties, properties of laplace transform, inverse laplace transform, characterization of LTI system, unilateral laplace transform |
2 days |
| Chapter 5 | Z-Transform
|
Introduction, ROC & its properties, properties of z-transform, inverse z-transform, function of discrete time LTI system, unilateral z-transform, relation between z and laplace transform |
2 days |
| Chapter 6 | Discrete Time Fourier Transform
|
Introduction to DTFT & its properties, DFT & its properties |
3 days |
| Chapter 7 | Sampling Theorem
|
Sampling theorem, ideal sampling, aliasing, sampling of bandpass signals |
3 days |
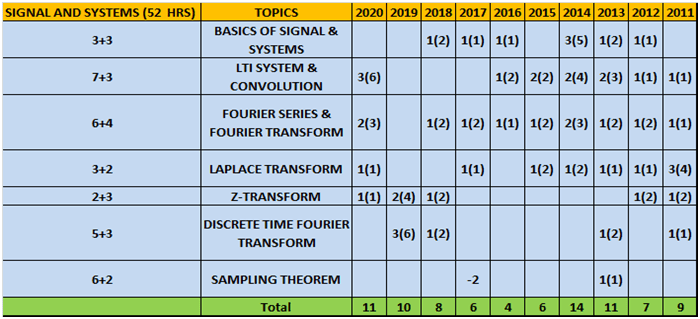
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Signals Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 52 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 5 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 8 | ||
| Total | 69hrs |
g. Analog
| Chapter 1 | Operational amplifier
|
Introduction, types of op-amp, voltage follower, current to voltage converter, voltage to current converter, filters, comparators, zero crossing detector, schmitt trigger, multivibrators, slew rate, CMRR, opamp parameters |
3 days |
| Chapter 2 | Diode applications
|
Introduction, rectifiers, clippers, clampers, voltage doubler, voltage regulator |
3 days |
| Chapter 3 | BJT biasing
|
Introduction, operating regions of transistor, modes of operations of BJT, load line, biasing |
2 days |
| Chapter 4 | Small signal analysis of BJT
|
Introduction,transistors at low and high frequency, T-model of BJT |
3 days |
| Chapter 5 | FET analysis
|
Introduction, JFET common source amplifier, JFET self-bias configuration |
3 days |
| Chapter 6 | Multistage amplifier
|
Introduction, lower cut-off frequency, cascode amplifiers, current mirror, darlington amplifier |
2 days |
| Chapter 7 | Feedback amplifier
|
Introduction, types of amplifiers, types of negative feedback, oscillators, audio and radio frequency oscillators |
3 days |
| Chapter 8 | Power amplifiers | Introduction, classification, collector efficiency, distortions |
3 days |
| Chapter 9 | 555 timer | Introduction, astablemultivibrator, monostablemultivibrator |
2 days |
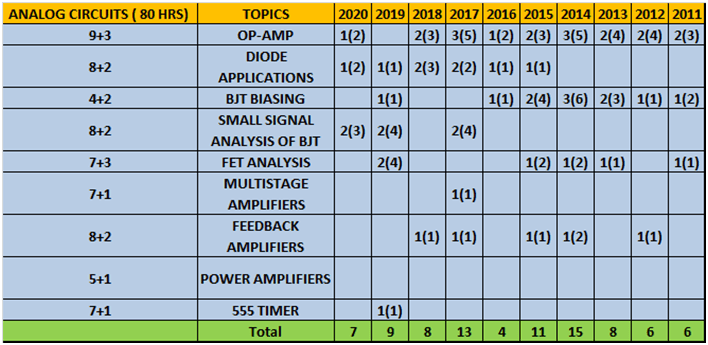
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Analog Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 80 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 5 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 8 | ||
| Total | 97hrs |
h. EMT
| Chapter 1 | Vectors and coordinate system
|
Vectors, coordinate systems and transformation, differential length, area and volume, del operator, classification of vector fields |
4 days |
| Chapter 2 | Electrostatics
|
Coulomb’s law, electric field intensity, Gauss’s law, electric potential, dipole, boundary conditions, continuity equation, poisson’s and laplace equations |
4 days |
| Chapter 3 | Magnetostatics
|
Introduction, Bio-Savart’s law, magnetic field intensity, ampere’s circuital law, magnetic flux density, force due to magnetic field, magnetic torque and moment, boundary conditions, inductance, magnetic energy |
3 days |
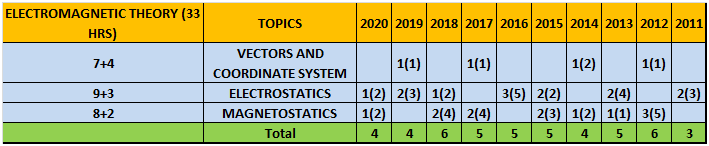
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Electromagnetic Theory Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 33 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 3 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 5 | ||
| Total | 45 hrs |
i. Measurement
| Chapter 1 | Characteristics, error standards
|
Measurements, classification of instruments, types of errors, standards |
1 day |
| Chapter 2 | Analog instruments
|
Introduction, indication instruments, types of supports, damping forces, electromechanical indicating instruments, PMMC instruments, DC ammeters, voltmeter multipliers, moving iron instruments & classification, electrodynamometer type, measurement of power and energy |
3 days |
| Chapter 3 | Measurement of resistance, inductance & capacitance
|
Classification of resistance, different methods of measurement, types of ohmmeter, bridge measurement, AC bridges, measurement of capacitance and frequency |
1 day |
| Chapter 4 | Cathode ray oscilloscope
|
Capacitance measurement, CRT, expression of electrostatic deflection, measurement using CRO, measurement of frequency, CRO, vertical input and sweep generator signal, blanking circuit |
2 days |
| Chapter 5 | Miscellaneous
|
Digital voltmeters, successive-approximations conversion, RAMP technique, dual slope integrating type DVM, resolutions and sensitivity of digital meters, block diagram of SA DVM |
1 days |
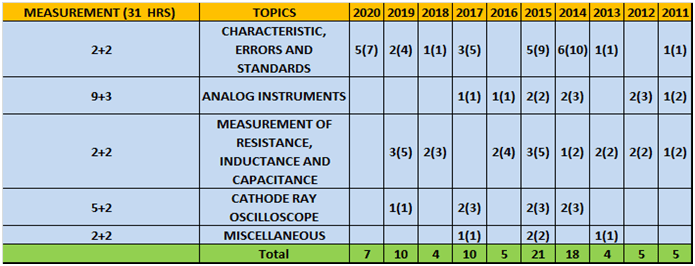
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Measurement Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 31 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 5 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 6 | ||
| Total | 46hrs |
j. Power Electronics
| Chapter 1 | Power semiconductor devices
|
Introduction, diodes & transistors, thyristors, UJT, comparison between GTO and thyristor, Comparison between thyristor and transistor, types of thyristors, gate/base commutating devices |
1 day |
| Chapter 2 | Phase controlled rectifiers
|
Single phase half wave rectifier, single phase full wave bridge converters, 3 phase converter, dual converter, performance parameters |
4 days
|
| Chapter 3 | Choppers
|
Introduction, step-up choppers, types of choppers, commutation |
2 days |
| Chapter 4 | Inverters
|
Introduction, single phase bridge inverter, 3 phase bridge inverter, PWM inverters |
2 days |
| Chapter 5 | Electrical drivers
|
Introduction, types of SMPS, uninterruptible power supplies, cycloconverter introduction, single phase to single phase circuit step-up cycloconverter, 3 phase half wave cycloconverters, AC voltage controller |
1 day |
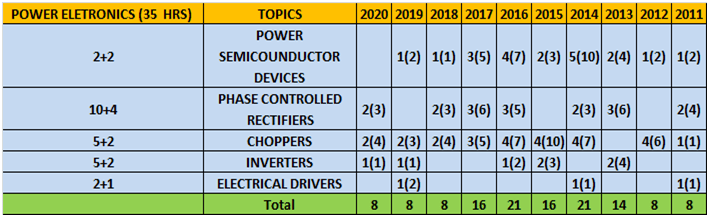
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Power Electronics Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 35 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 7 | ||
| Total | 50hrs |
k. Power Systems
| Chapter 1 | Transmission line model and performance
|
Introduction, flux linkages, inductance of two wire transmission line, transposition of power lines, composite conductors, concept of geometric mean distance, skin and proximity effect, capacitance of transmission lines, performance of lines, constants for two networks in tandem and parallel, ferranti effect |
3 days |
| Chapter 2 | Corona, insulators, cables
|
Insulation, insulated cables, grading of cables, extra high voltage cables, insulation resistance and capacitance of a cable, heating of cables, corona, factors effecting corona loss |
2 days |
| Chapter 3 | Per unit system, symmetrical components, fault analysis
|
Introduction, symmetric fault analysis, transient on a transmission line, short circuit of loaded and no load synchronous machine, fault analysis and symmetrical components |
3 days |
| Chapter 4 | Power system stability
|
Introduction, synchronous machine, power system synchronous stability, power system stability |
2 days |
| Chapter 5 | Load flows, economic load dispatch, load frequency control
|
Introduction, newton-raphson method, load flows, iterative methods, economic load dispatch |
4 days |
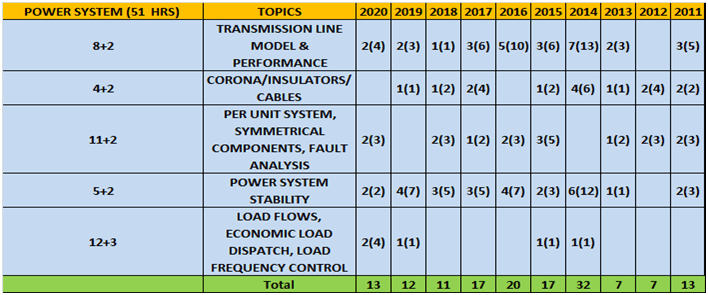
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Power System Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 51 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 5 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 5 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 8 | ||
| Total | 69hrs |
l. Electrical Machines
| Chapter 1 | DC machines
|
DC generators, types of generator, emf equations of generators, ron loss in armature, total loss in DC generator, armature reaction, commutation, characteristics of DC generator compound-wound generator, DC motor & its characteristics, performance curves, speed control of dc and series motors, electric braking, testing of DC machines |
3 days |
| Chapter 2 | Transformers
|
Introduction, transformer-construction, principle, equivalent circuit, voltage regulation, losses, efficiency, tests, auto transformers, 3 phase transformers |
4 days |
| Chapter 3 | Induction motors
|
Introduction, losses and efficiency, phasor diagram, equivalent circuit, rotor circuit model, torque slip and power slip characteristics, operating characteristics, induction motor stability, circle diagram, power factor control, starting of polyphase induction motors, induction motor stability, induction generator, crawling, cogging or magnetic locking, double squirrel cage motor |
4 days |
| Chapter 4 | Synchronous machines
|
Introduction, circuit model, characteristics, SCR, Potier method, operating characteristics, power flow equations, capability curve of synchronous generator, power angle characteristics, parallel operations, hunting, damper winding, special machines |
4 days |
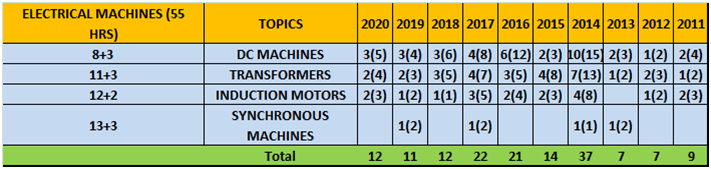
- Column 1 represents Time to study and make notes + Solving GATE Questions of that topic .
- The last 10 columns represent year wise number questions( marks in Bracket ).
|
Electrical Machines Master Plan
|
Hours | Remarks | |
| Notes + Gate Questions | 55 | ||
| Topic test from Aspiration.ai | 5 | with Analysis | |
| Subject test from aspiration.ai | 4 | with Analysis | |
| revision overall | 8 | ||
| Total | 72hrs |